Google Analytics Standards: What Data Does Google Analytics Prohibit Collecting?
Google Analytics Standards: What Data Does Google Analytics Prohibit Collecting?
Blog Article
Recognizing the Ins and Outs of Information Collection Limitations in Google Analytics to Enhance Your Insights
Navigating the landscape of information collection within Google Analytics reveals a myriad of complexities that can dramatically affect the insights acquired from your digital analytics. As organizations progressively depend on data-driven decision-making, understanding the restrictions and subtleties of data collection comes to be paramount. From data tasting in reports to the difficulties presented by cross-domain monitoring and the rise of advertisement blockers, each variable adds layers of ins and out to the precision and deepness of the information at hand. However, the genuine intrigue depends on exactly how these limitations can be not just recognized however strategically maneuvered to elevate the quality and dependability of the understandings you extract from your analytics initiatives.
Information Testing in Records
When assessing information in Google Analytics, one critical facet to consider is the existence of data tasting in records, which can influence the precision and reliability of insights derived from the data. Information tasting is a strategy utilized to analyze a part of data rather than the full dataset.
The effects of information sampling can be substantial, specifically when making crucial service choices based upon the analytics information. Tasting can result in skewed outcomes and false impressions, especially in analyses requiring a granular view of individual actions or efficiency metrics. To minimize the impact of data sampling, it is necessary to comprehend when sampling happens, check the tasting price in records, and take into consideration buying Google Analytics 360, which offers higher handling limits to lower the demand for tasting. By knowing information tasting in records, analysts can make even more educated choices based on precise data insights.
Cross-Domain Monitoring Difficulties
Cross-domain monitoring presents a facility collection of difficulties that can impact the accuracy and reliability of data aggregation in Google Analytics. When tracking individuals across numerous domain names, issues can arise due to differences in domain frameworks, cookie setups, and monitoring codes. Among the key difficulties of cross-domain tracking is making certain that a solitary user is correctly recognized as they move from one domain to another. Without proper configuration, Google Analytics may analyze these interactions as separate sessions, causing data fragmentation and inaccurate insights.
Failure to carry out these changes appropriately can result in data disparities and insufficient tracking, impeding the capacity to understand individual behavior flawlessly across domain names. Conquering these obstacles needs extensive preparation, precise application, and constant surveillance to make sure data precision and derive purposeful insights across domains in Google Analytics.
Impact of Ad Blockers
The occurrence of advertisement blockers poses substantial challenges to data collection accuracy in Google Analytics (What Data Does Google Analytics Prohibit Collecting?). Advertisement blockers are browser extensions or software that customers mount to protect against ads from showing on web sites. These devices not just obstruct promotions yet can also hinder the tracking codes used by Google Analytics to collect data. Because of this, site proprietors may experience discrepancies in their analytics records, causing insufficient or incorrect data.
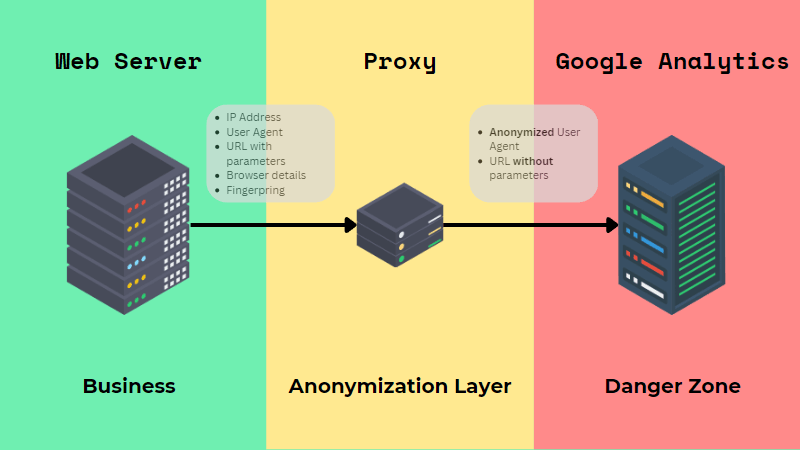
To mitigate the effect of ad blockers on information collection, website proprietors can explore different monitoring techniques, such as server-side tracking or executing permission monitoring devices to urge users to disable advertisement blockers on their websites. By proactively resolving the challenges postured by ad blockers, organizations can boost the precision of their information collection in Google Analytics and enhance their general understanding of individual behavior.

Cookie Removal Effects
Periodically, cookie deletion can affect the dependability of information collected by Google Analytics, affecting the accuracy of site traffic evaluation. Cookies are little pieces of data saved on a customer's gadget that help track their on-line behavior. When users delete cookies, it can disrupt the tracking process, leading to spaces in data collection. This can lead to manipulated analytics records, as returning site visitors may be counted as new ones after cookie removal. Moreover, if a considerable variety of individuals on a regular basis erase cookies, it can make it challenging to track customer journeys precisely and recognize their interactions with the web site. As a result, services might make choices based upon inaccurate or incomplete information, influencing their marketing techniques and general efficiency evaluation. To mitigate the effects of cookie deletion, it is essential to enhance cookie-based data with various other tracking techniques, such as server-side monitoring or integrating first-party information resources, to guarantee a much more extensive understanding of individual behavior.
Data Privacy Regulations
Because of boosting issues surrounding information privacy and defense, services using Google Analytics must stick to rigid information privacy regulations to ensure compliance and secure user details. One of the key laws that influence information collection methods is the General Data Defense Policy (GDPR) implemented by the European Union. GDPR requireds that companies obtain specific permission from users before accumulating and processing their personal information. This consists of information gathered via Google Analytics, such as IP addresses or surfing behavior. Furthermore, services should provide customers with the alternative to opt-out of monitoring systems, better stressing the significance of openness and customer control.
Aside From GDPR, there are other data privacy laws like the California Customer Personal Privacy Act (CCPA) and the ePrivacy Directive that businesses require to take into consideration when using Google Analytics. These policies aim to shield individual data and provide people more control over just how their info is gathered and used. By comprehending and conforming with these information privacy guidelines, businesses can build trust with their users and show a commitment to information defense and personal privacy.
Verdict
Finally, recognizing the constraints of information collection in Google Analytics is vital for boosting insights. Information tasting in reports, cross-domain monitoring challenges, the influence of ad blockers, cookie deletion impacts, and article source information privacy regulations all contribute in the accuracy and completeness of the information gathered. By knowing these limitations and discovering methods to mitigate them, businesses can ensure they are making educated decisions based on trusted data.
When examining information in Google Analytics, one important aspect to take into consideration is the existence of data tasting in records, which can impact the accuracy and reliability of insights acquired from the data. To mitigate the results of cookie deletion, it is crucial to match cookie-based data with various other tracking he said approaches, such as server-side monitoring or incorporating first-party information resources, to make sure a more extensive understanding of user actions.
Information sampling in reports, cross-domain monitoring difficulties, the influence of advertisement blockers, cookie deletion effects, and data personal privacy policies all play a function find more information in the precision and efficiency of the information collected.
Report this page